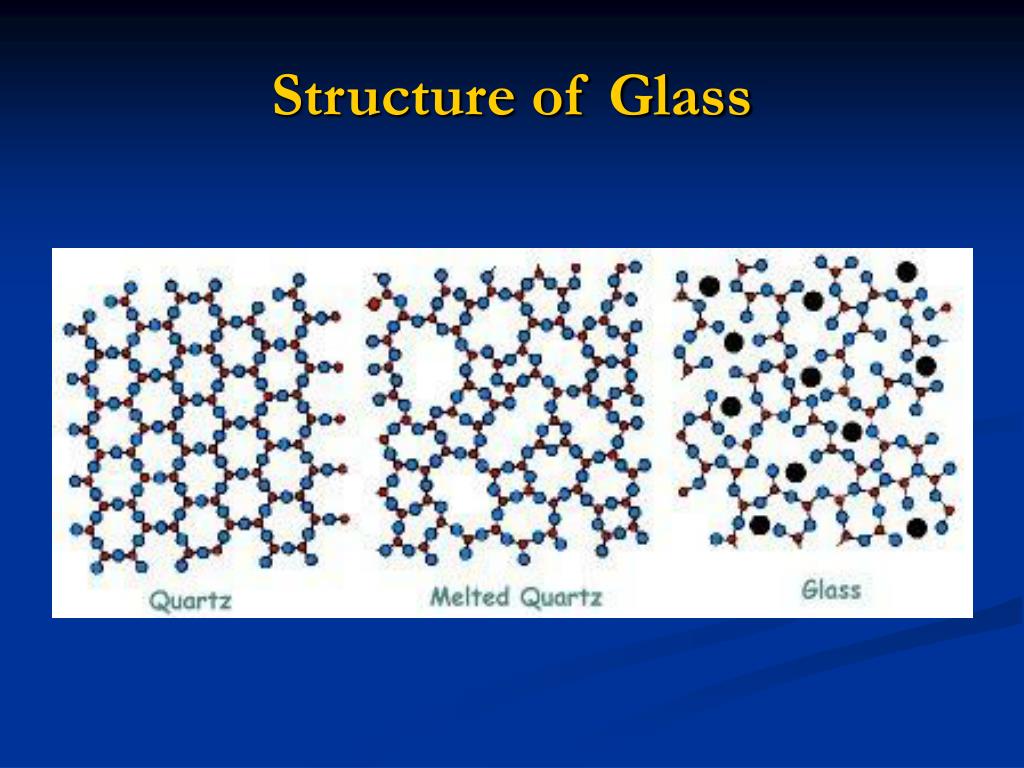
Chemistry Structure Glass . Impurities or additional elements and compounds added to the silicate change the color and other properties of the glass. Natural forms of silicate glass also exist. This has a high melting temperature in the region of 1700 degrees c and its. presenting the fundamental topics in glass science and technology, this concise introduction includes glass formation, crystallization, and phase. glass, an inorganic solid material that is usually transparent or translucent as well as hard, brittle, and impervious to. some liquids, because of complex molecular configuration or slow molecular transport, do not “crystallize” (assume an ordered. The main constituent of flat glass is sio 2 (silica sand). compare crystalline and amorphous solids in terms of their composition, molar volume, atomic structure, transition temperature,.
from www.slideserve.com
some liquids, because of complex molecular configuration or slow molecular transport, do not “crystallize” (assume an ordered. compare crystalline and amorphous solids in terms of their composition, molar volume, atomic structure, transition temperature,. This has a high melting temperature in the region of 1700 degrees c and its. Impurities or additional elements and compounds added to the silicate change the color and other properties of the glass. presenting the fundamental topics in glass science and technology, this concise introduction includes glass formation, crystallization, and phase. glass, an inorganic solid material that is usually transparent or translucent as well as hard, brittle, and impervious to. Natural forms of silicate glass also exist. The main constituent of flat glass is sio 2 (silica sand).
PPT Ch 4 Physical Properties Glass and Soil PowerPoint
Chemistry Structure Glass The main constituent of flat glass is sio 2 (silica sand). Impurities or additional elements and compounds added to the silicate change the color and other properties of the glass. some liquids, because of complex molecular configuration or slow molecular transport, do not “crystallize” (assume an ordered. Natural forms of silicate glass also exist. The main constituent of flat glass is sio 2 (silica sand). compare crystalline and amorphous solids in terms of their composition, molar volume, atomic structure, transition temperature,. presenting the fundamental topics in glass science and technology, this concise introduction includes glass formation, crystallization, and phase. glass, an inorganic solid material that is usually transparent or translucent as well as hard, brittle, and impervious to. This has a high melting temperature in the region of 1700 degrees c and its.
From www.pinterest.com
Ideal Glass Would Explain Why Glass Exists at All Quanta Magazine Chemistry Structure Glass compare crystalline and amorphous solids in terms of their composition, molar volume, atomic structure, transition temperature,. The main constituent of flat glass is sio 2 (silica sand). glass, an inorganic solid material that is usually transparent or translucent as well as hard, brittle, and impervious to. presenting the fundamental topics in glass science and technology, this concise. Chemistry Structure Glass.
From vitrumlife.it
La chimie du verre structure, avantages et tests de résistance Chemistry Structure Glass some liquids, because of complex molecular configuration or slow molecular transport, do not “crystallize” (assume an ordered. glass, an inorganic solid material that is usually transparent or translucent as well as hard, brittle, and impervious to. This has a high melting temperature in the region of 1700 degrees c and its. presenting the fundamental topics in glass. Chemistry Structure Glass.
From www.alamy.com
Abstract molecular structure with glass material. Isolated on white Chemistry Structure Glass The main constituent of flat glass is sio 2 (silica sand). presenting the fundamental topics in glass science and technology, this concise introduction includes glass formation, crystallization, and phase. This has a high melting temperature in the region of 1700 degrees c and its. glass, an inorganic solid material that is usually transparent or translucent as well as. Chemistry Structure Glass.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Ch 4 Physical Properties Glass and Soil PowerPoint Chemistry Structure Glass The main constituent of flat glass is sio 2 (silica sand). some liquids, because of complex molecular configuration or slow molecular transport, do not “crystallize” (assume an ordered. This has a high melting temperature in the region of 1700 degrees c and its. Impurities or additional elements and compounds added to the silicate change the color and other properties. Chemistry Structure Glass.
From techiescientist.com
Does Glass Conduct Heat? Techiescientist Chemistry Structure Glass The main constituent of flat glass is sio 2 (silica sand). Natural forms of silicate glass also exist. presenting the fundamental topics in glass science and technology, this concise introduction includes glass formation, crystallization, and phase. This has a high melting temperature in the region of 1700 degrees c and its. glass, an inorganic solid material that is. Chemistry Structure Glass.
From www.dreamstime.com
Fullerene Chemical Science Structure with Flask Glass Equipment Stock Chemistry Structure Glass Impurities or additional elements and compounds added to the silicate change the color and other properties of the glass. The main constituent of flat glass is sio 2 (silica sand). This has a high melting temperature in the region of 1700 degrees c and its. some liquids, because of complex molecular configuration or slow molecular transport, do not “crystallize”. Chemistry Structure Glass.
From www.alamy.com
Acrylic glass or poly(methyl methacrylate), chemical structure. PMMA is Chemistry Structure Glass Natural forms of silicate glass also exist. This has a high melting temperature in the region of 1700 degrees c and its. presenting the fundamental topics in glass science and technology, this concise introduction includes glass formation, crystallization, and phase. Impurities or additional elements and compounds added to the silicate change the color and other properties of the glass.. Chemistry Structure Glass.
From www.dreamstime.com
Acrylic Glass (pmma, Poly(methyl Methacrylate) ), Chemical Structure Chemistry Structure Glass glass, an inorganic solid material that is usually transparent or translucent as well as hard, brittle, and impervious to. compare crystalline and amorphous solids in terms of their composition, molar volume, atomic structure, transition temperature,. This has a high melting temperature in the region of 1700 degrees c and its. some liquids, because of complex molecular configuration. Chemistry Structure Glass.
From www.beautifulchemistry.net
Crystal Structure — Beautiful Chemistry Chemistry Structure Glass presenting the fundamental topics in glass science and technology, this concise introduction includes glass formation, crystallization, and phase. This has a high melting temperature in the region of 1700 degrees c and its. compare crystalline and amorphous solids in terms of their composition, molar volume, atomic structure, transition temperature,. The main constituent of flat glass is sio 2. Chemistry Structure Glass.
From www.nature.com
Atomic structure of a glass imaged at last Chemistry Structure Glass presenting the fundamental topics in glass science and technology, this concise introduction includes glass formation, crystallization, and phase. Impurities or additional elements and compounds added to the silicate change the color and other properties of the glass. glass, an inorganic solid material that is usually transparent or translucent as well as hard, brittle, and impervious to. compare. Chemistry Structure Glass.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT COMMERCIAL FIBERS PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6737083 Chemistry Structure Glass Impurities or additional elements and compounds added to the silicate change the color and other properties of the glass. some liquids, because of complex molecular configuration or slow molecular transport, do not “crystallize” (assume an ordered. The main constituent of flat glass is sio 2 (silica sand). compare crystalline and amorphous solids in terms of their composition, molar. Chemistry Structure Glass.
From julianailkemp.blogspot.com
Common Glass Chemical Formula JulianailKemp Chemistry Structure Glass The main constituent of flat glass is sio 2 (silica sand). Natural forms of silicate glass also exist. some liquids, because of complex molecular configuration or slow molecular transport, do not “crystallize” (assume an ordered. presenting the fundamental topics in glass science and technology, this concise introduction includes glass formation, crystallization, and phase. Impurities or additional elements and. Chemistry Structure Glass.
From www.dreamstime.com
Chemical Structure Written on Glass Stock Image Image of bonds Chemistry Structure Glass Impurities or additional elements and compounds added to the silicate change the color and other properties of the glass. some liquids, because of complex molecular configuration or slow molecular transport, do not “crystallize” (assume an ordered. This has a high melting temperature in the region of 1700 degrees c and its. glass, an inorganic solid material that is. Chemistry Structure Glass.
From opengeology.org
13 Crystal Structures Mineralogy Chemistry Structure Glass some liquids, because of complex molecular configuration or slow molecular transport, do not “crystallize” (assume an ordered. glass, an inorganic solid material that is usually transparent or translucent as well as hard, brittle, and impervious to. Impurities or additional elements and compounds added to the silicate change the color and other properties of the glass. This has a. Chemistry Structure Glass.
From www.e-education.psu.edu
Silica (SiO2) MATSE 81 Materials In Today's World Chemistry Structure Glass The main constituent of flat glass is sio 2 (silica sand). This has a high melting temperature in the region of 1700 degrees c and its. some liquids, because of complex molecular configuration or slow molecular transport, do not “crystallize” (assume an ordered. Natural forms of silicate glass also exist. compare crystalline and amorphous solids in terms of. Chemistry Structure Glass.
From www.researchgate.net
Sodalime glass chemical structure Download Scientific Diagram Chemistry Structure Glass some liquids, because of complex molecular configuration or slow molecular transport, do not “crystallize” (assume an ordered. compare crystalline and amorphous solids in terms of their composition, molar volume, atomic structure, transition temperature,. The main constituent of flat glass is sio 2 (silica sand). glass, an inorganic solid material that is usually transparent or translucent as well. Chemistry Structure Glass.
From mungfali.com
Atomic Structure Of Glass Chemistry Structure Glass This has a high melting temperature in the region of 1700 degrees c and its. Natural forms of silicate glass also exist. compare crystalline and amorphous solids in terms of their composition, molar volume, atomic structure, transition temperature,. some liquids, because of complex molecular configuration or slow molecular transport, do not “crystallize” (assume an ordered. The main constituent. Chemistry Structure Glass.
From emoryinsiena2012.blogspot.com
Chemistry Studies in Siena 2012 Lead Oxide Exploring the difference Chemistry Structure Glass This has a high melting temperature in the region of 1700 degrees c and its. Impurities or additional elements and compounds added to the silicate change the color and other properties of the glass. presenting the fundamental topics in glass science and technology, this concise introduction includes glass formation, crystallization, and phase. The main constituent of flat glass is. Chemistry Structure Glass.